Case Studies & Real-World Implementation Challenges in Water Reuse: Lecture 9
Overall Goal: To bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application by examining successful water reuse initiatives in the textile industry, highlighting common challenges and effective solutions in real-world settings.
9.1. The Journey from Design to Operation: Bridging Theory and Practice
- Recap of Treatment Train: Briefly review the multi-stage treatment process (primary, secondary, tertiary) and conditioning for reuse.
- The “Valley of Death” in Implementation: Discuss the gap between successful pilot projects/design and full-scale operational reality.
- Importance of Context: Emphasize that every textile plant is unique (raw material, product type, scale, location, existing infrastructure), meaning there’s no one-size-fits-all solution for water reuse.
9.2. Detailed Case Studies: Diverse Approaches to Textile Water Reuse
We will explore 2-3 detailed case studies, preferably from various regions (e.g., one from Pakistan, one from another developing country, one from a developed country with stringent regulations) to showcase different scales, technologies, and challenges. For each case study, we will cover:
- Company Profile: Type of textile production (e.g., denim, knitwear, dyeing & finishing house).
- Initial Water Footprint: How much fresh water was consumed and wastewater discharged before reuse implementation.
- Chosen Treatment Technologies: The specific primary, secondary, and tertiary/advanced technologies implemented, and why they were selected.
- Achieved Water Quality: What quality of water is produced and for what specific processes it is reused (e.g., washing, mercerizing, dyeing, boiler feed).
- Economic & Environmental Impact: Quantifiable savings (water, energy, chemicals) and reductions in pollution.
- Key Success Factors: What made their project successful (e.g., strong management commitment, skilled team, robust technology selection, good integration).
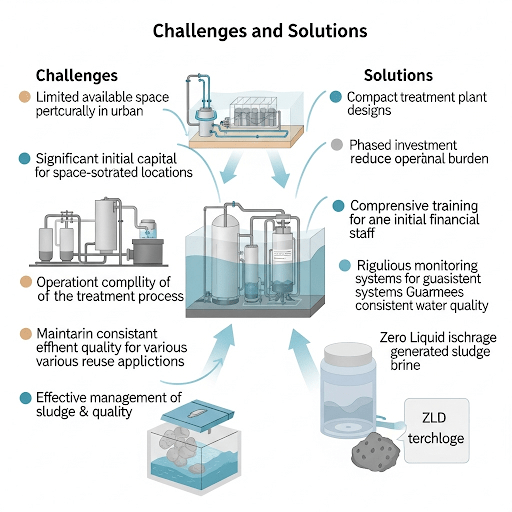
9.3. Common Implementation Challenges & Mitigation Strategies
This section will delve into the practical hurdles often faced during the implementation of water reuse projects in the textile sector:
- Space & Infrastructure Constraints:
- Challenge: Many existing textile mills are old with limited space for new treatment units. Integrating new systems with old piping and utilities.
- Mitigation: Compact designs (e.g., MBR, lamella clarifiers, containerized units), phased implementation, careful brownfield integration planning.
- Capital Investment & Financial Hurdles:
- Challenge: High upfront costs, difficulty securing financing, long payback periods.
- Mitigation: Detailed cost-benefit analysis (as discussed in Lecture 7), exploring government incentives/subsidies, phased investment, Build-Own-Operate (BOO) or Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT) models with third-party providers.
- Operational & Maintenance Complexity:
- Challenge: Advanced technologies require skilled operators, increased maintenance, managing membrane fouling, chemical dosing calibration.
- Mitigation: Comprehensive operator training programs, robust automation (Lecture 8), preventative maintenance schedules, strong technical support from vendors, designing for ease of maintenance.
- Water Quality Consistency & Process Interference:
- Challenge: Variable influent quality leading to inconsistent treated water; residual contaminants (e.g., trace dyes, heavy metals) affecting sensitive dyeing processes.
- Mitigation: Robust equalization (Lecture 2), online monitoring and adaptive control (Lecture 8), pre-treatment for specific problematic streams, redundant treatment units, bypass options for off-spec water.
- Sludge & Brine Management:
- Challenge: The cost and environmental burden of managing solid sludge and highly concentrated liquid brine from RO.
- Mitigation: Optimizing dewatering, exploring co-processing or energy recovery from sludge, investing in ZLD for brine if feasible and regulatory drivers are strong.
- Social & Acceptance Factors:
- Challenge: Resistance from workers or management due to fear of change, perceived risks to product quality, or lack of understanding.
- Mitigation: Transparent communication, pilot studies to demonstrate efficacy, training and involvement of all stakeholders, showcasing successful internal or external case studies.
9.4. Towards Sustainable Textile Production: Lessons Learned
- Key Takeaways: Summarize the critical success factors for textile water reuse projects (e.g., holistic planning, strong financial justification, robust technology selection, skilled workforce, continuous monitoring).
- Continuous Improvement: Emphasize that water reuse is an ongoing process of optimization and adaptation.
- Future Outlook: Briefly touch upon the increasing importance of water circularity and resource efficiency in the global textile industry, positioning water reuse as a cornerstone of sustainable manufacturing.
